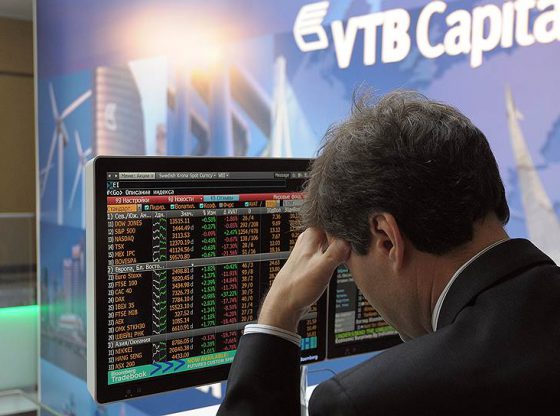
VTB, one of the bidders for India’s Essar Steel, has faced charges in the US. In 2016, the US Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) fined VTB Bank and its subsidiary VTB Capital a combined $5 million for executing fictitious and non-competitive trades. The trades were executed at higher prices than VTB would have obtained from third parties. The US government authority declared VTB guilty of illegal financial transactions. CFTC ordered VTB Bank and VTB Capital to jointly and severally pay a civil monetary penalty of $5 million as a result of their unlawful conduct.
VTB’s operations under US scrutiny
In 2016 the US Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) charged Sankt Petersburg-based VTB Bank and London-based VTB Capital with serious claims for several transactions. CFTC found that between December 2010 and June 2013 the banks violated the Commodity Exchange Act, executing over 100 block trades in Russian Rubble/US Dollar. These block trades had a total value of approximately $36 billion. The UK Financial Conduct Authority provided assistance to CFTC in this case.
CFTC is a US government authority that regulates the US derivatives markets, including futures, options, and swaps. Its mission is to promote market integrity and protect the market users, consumers, and the public from fraud, manipulation, and abusive practices.
The state-owned VTB Bank is Russia’s second largest bank and the parent company of VTB Group. VTB Capital is 94% owned by a holding company that is 100% owned by VTB Bank. VTB Bank and its subsidiaries, including VTB Capital, are subject to international sanctions over Russia’s annexation of Crimea.
VTB Group’s fictitious deals
The Commission found that VTB Bank – VTB Capital’s block trades contracts constituted fictitious sales under the Commodity Exchange Act. According to the US regulator, VTB recorded prices that were not true and bona fide prices. The prices utilised by VTB and its subsidiary were not fair or reasonable because they did not take into account the circumstances of the markets. The trades were executed at higher prices than VTB would have obtained from third parties. The transactions were noncompetitively priced and designed to avoid market risk.
The transactions constituted unlawful non-competitive trades. Through the block trades, VTB was able to transfer its cross-currency risk to its subsidiary, VTB Capital, which could then hedge the risk in the swap markets.
A $5 Million penalty for unlawful conduct
CFTC declared VTB Group guilty of illegal financial transactions involving Russian rubble futures.
On 19 September 2016, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission issued an Order Instituting Proceeding Pursuant to Sections 6(c) and 6(d) of the Commodity Exchange Act, Making Findings and Imposing Remedial Sanctions.
CFTC Order VTB – click here to see more
CFTC found that VTB Bank and VTB Capital violated the Commodity Exchange Act and Commission Regulation and imposed remedial sanctions. CFTC ordered VTB Bank and VTB Capital to cease and desist violating the Commodity Exchange Act. The US regulator ordered Russian companies to jointly and severally pay a civil monetary penalty of $5 million as a result of their unlawful conduct.
In addition to the $5 million fine, the banks were banned from entering into privately negotiated futures, options or combination transactions with one another on or through any US-based futures exchange for a period of two years. The order also demanded VTB and VTB Capital to submit a confidential report outlining the steps they have taken to comply with CFTC’s order.
The order filed and simultaneously settled charges against VTB Group. In anticipation of an administrative proceeding resulting from VTB Bank and VTB Capital’s violations of the Commodity Exchange Act, the Russian companies submitted an offer of settlement for $5 million, which the Commission accepted.